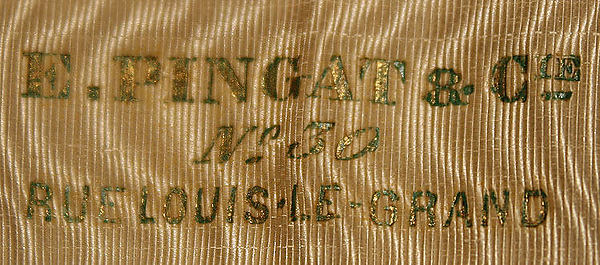About the Designer
Amaster dressmaker and designer, Emile Pingat (c. 1820-1901) was among the elite Paris couturiers of his age, who dressed the wealthiest and most sophisticated of clients in the fashion capital of the world. His celebrity was evident in the fashion press and his mastery of his craft was demonstrated in every elegant silk gown and trimming that he created.
By 1864, Pingat opened his couture house at 30 Rue Louis-Le-Grand in Paris and he quickly became a competitor Charles Fredrick Worth. His clients knew him for flawless workmanship and monochromatic color palettes enlivened with a single accent color, which gave his works elegance without sacrificing any of the opulence of nineteenth-century fashion. Americans who visited Paris liked to fill their trunks with haute couture and often frequented the Maison Pingat; for those who could not make the journey to Paris, licensed copies of Pingat’s designs were made to order by American dressmakers and stores. Fashion-conscious women could also make their own versions of Pingat originals thanks to sewing patterns sold by Harper’s Bazar.
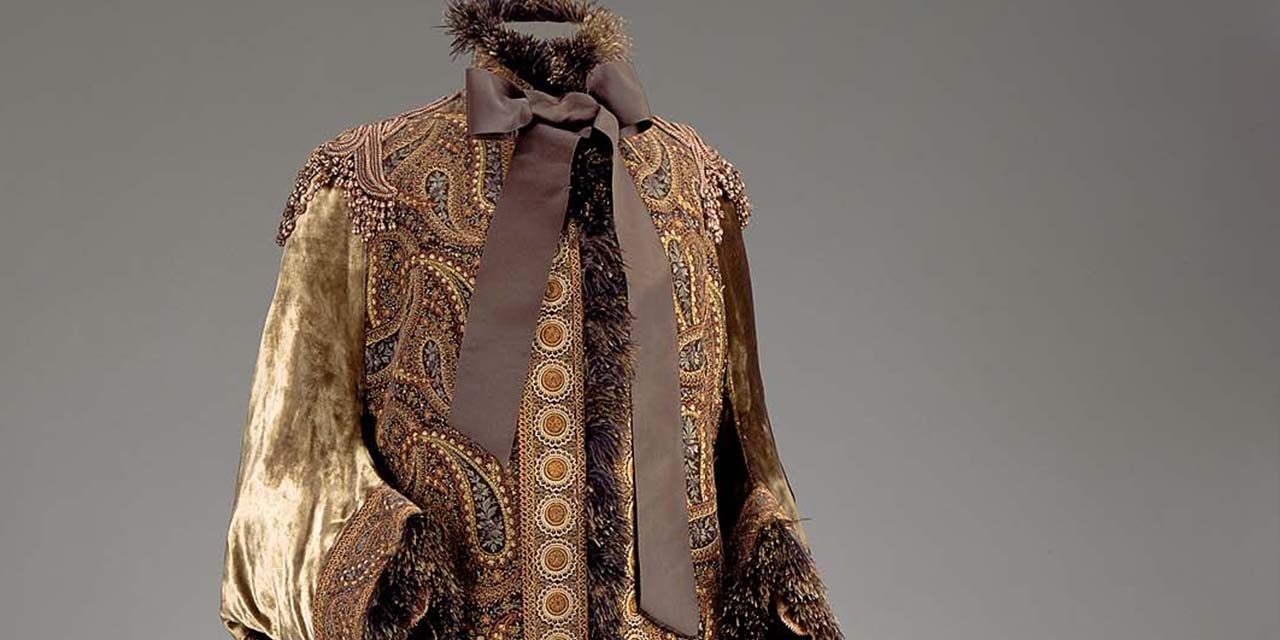
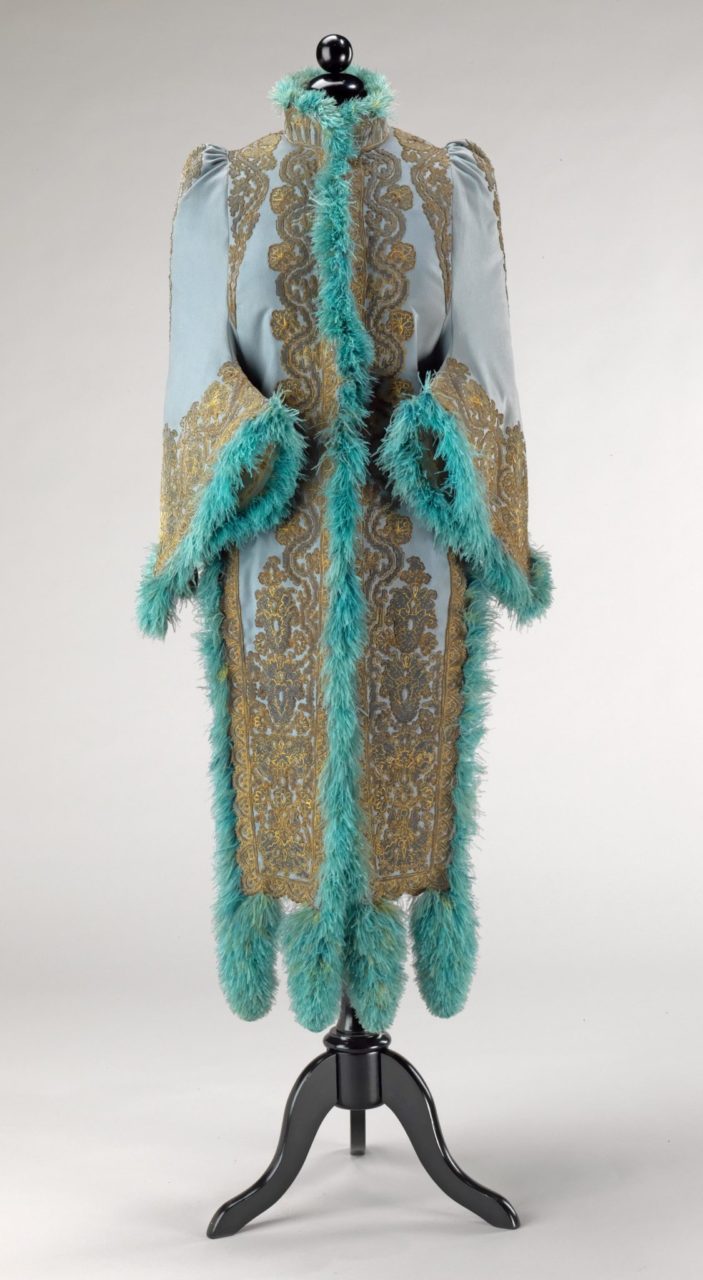
By the 1880s, Pingat was known for his outerwear, including day and evening cloaks, jackets, and dolmans. While cloaks and jackets are still worn today, the dolman was an outer garment designed to accommodate the large bustle of the 1880s, and the term is used for any outer garment designed with the bustle in mind. Pingat designed his outerwear with no less artistry than his other creations, masterfully combining sumptuous silks and unusual trimmings such as feathers and fur with delicate embroideries and lace.
Despite coverage in the fashion press and extant garments that show Pingat was a fashion giant and among the first couturiers, relatively little is known about him.
Style
Pingat was known for his deft manipulation of textiles, showing off their beauty to create elegant garments with a single base color and a single accent color. He chose colors and trimmings that are artistic but never excessive. Note in particular Pingat’s use of negative spaces contrasted with bold trimmings, layered ruffles, and embroideries on voluminous skirts.
Timeline Essays (Click the images to read more):
GALLERY
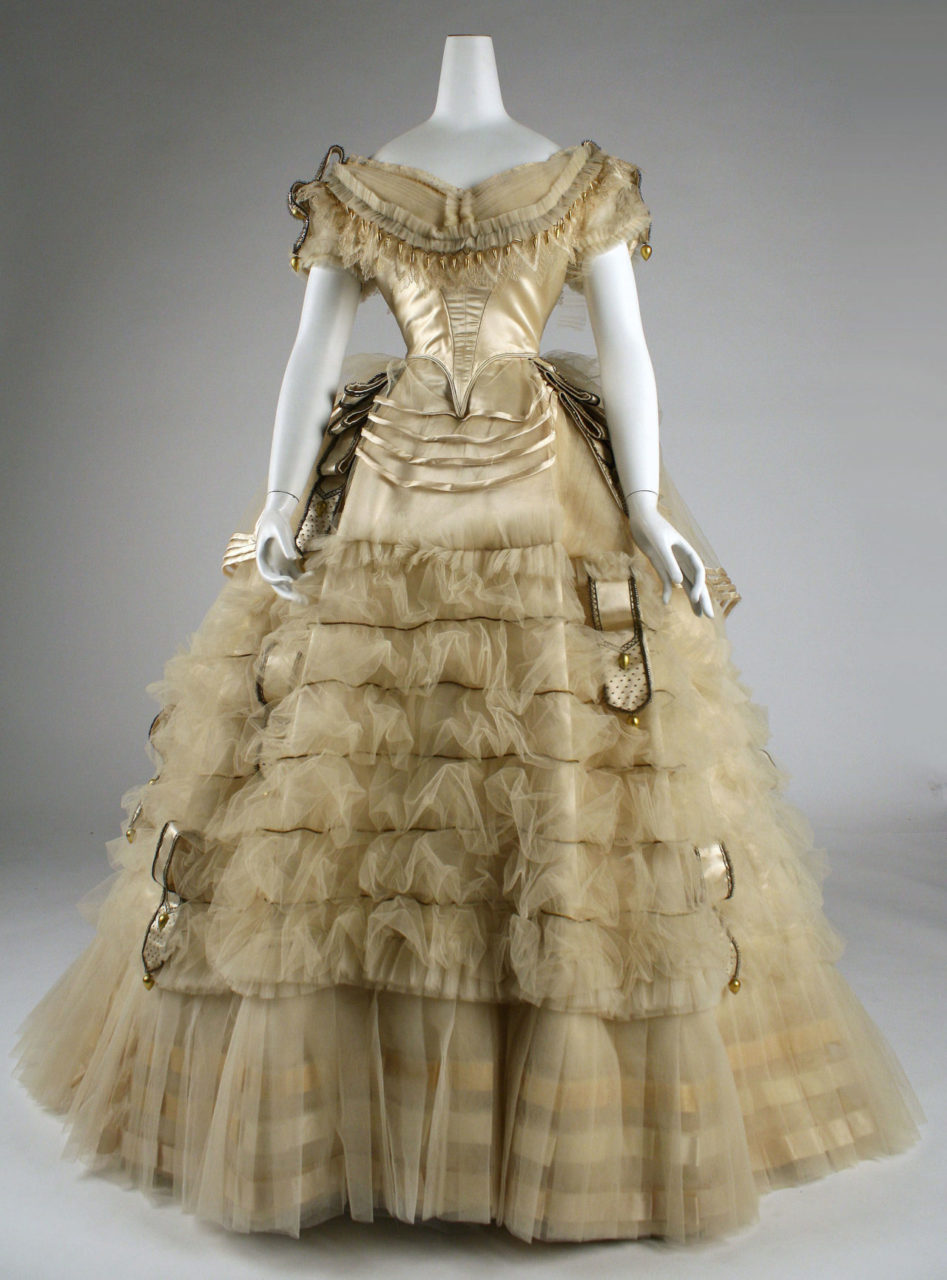
Emile Pingat (French, 1820-1901). Ball gown, ca. 1860. Silk. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, C.I.69.33.1a, b. Gift of Mary Pierrepont Beckwith, 1969. Source: The Met
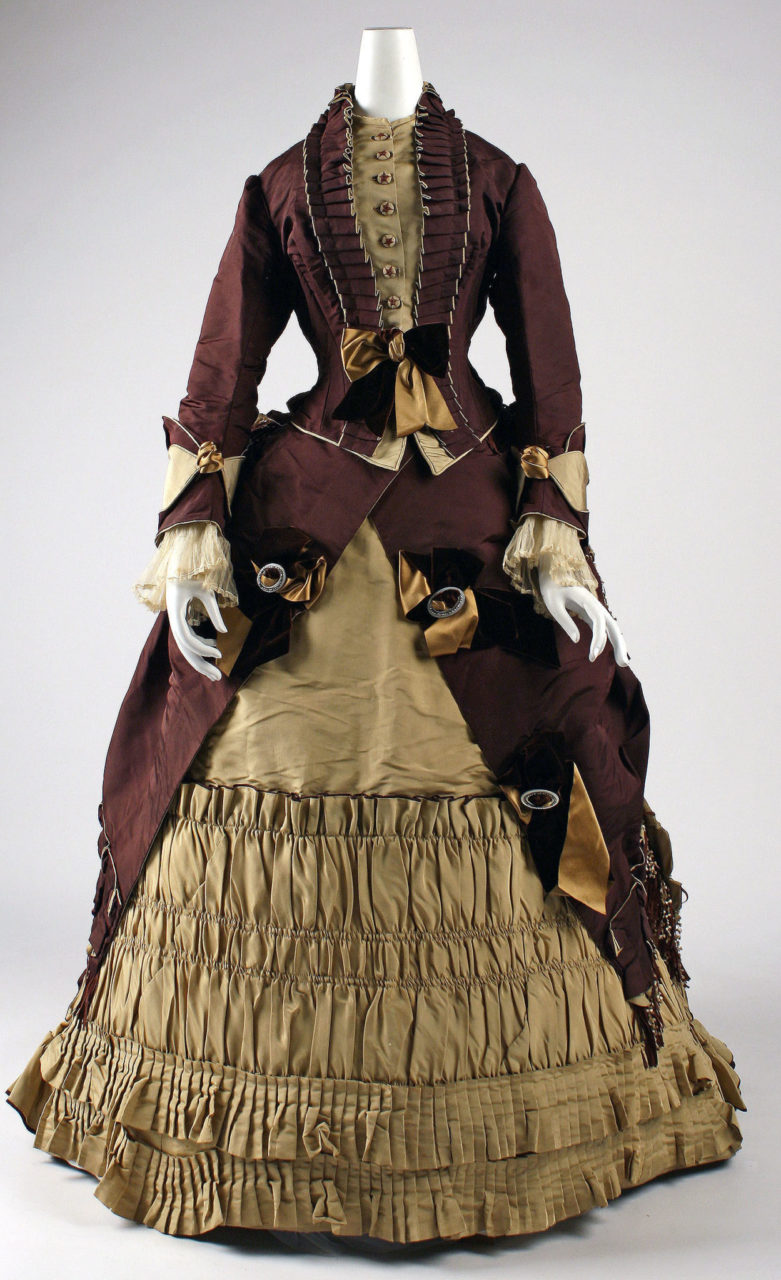
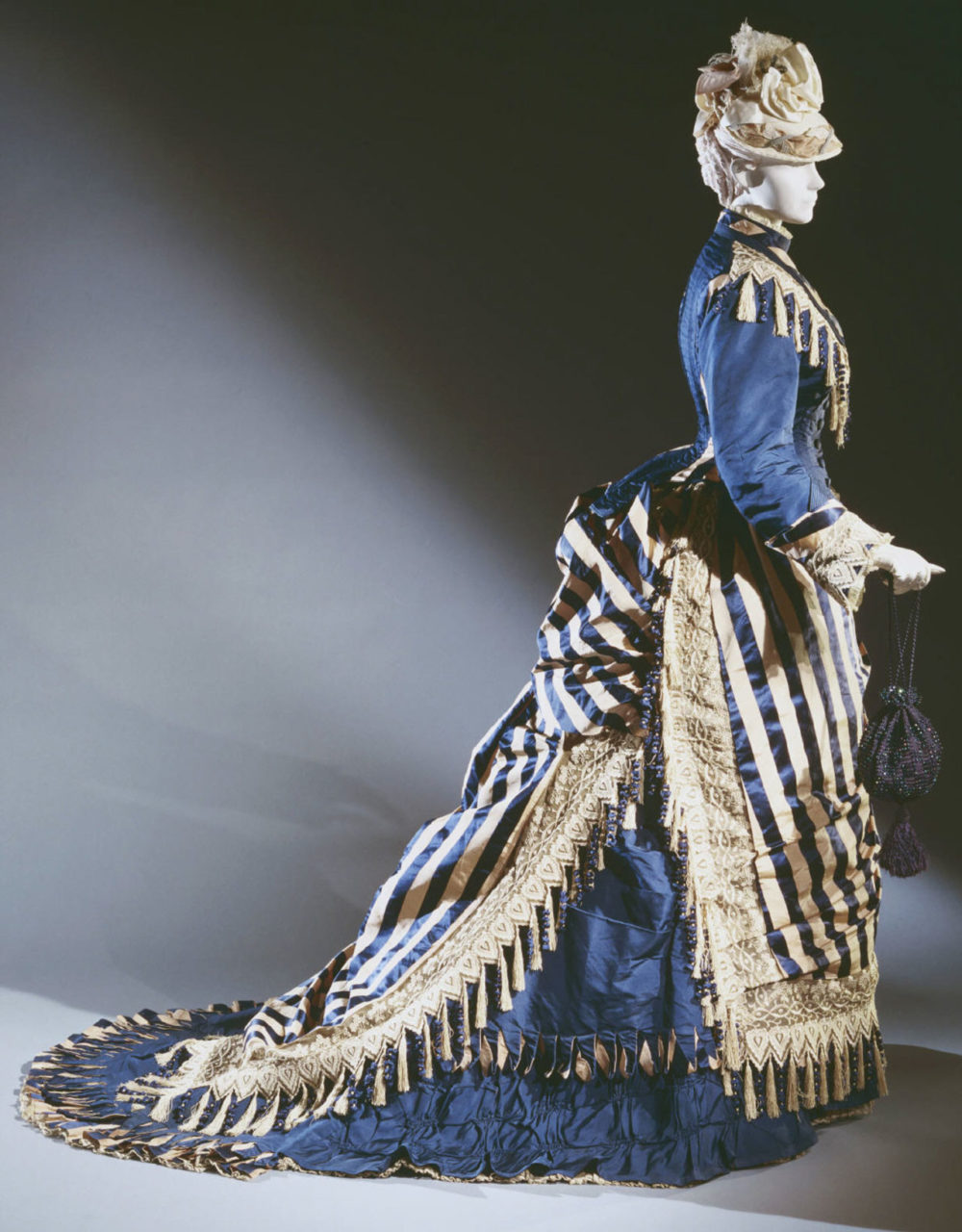
Emile Pingat (French, 1820-1901). Woman's reception dress (bodice and skirt), ca. 1874. Silk with stripes of dark blue satin and tan plain weave; dark blue silk faille; ivory silk embroidery on silk net; ivory and dark blue silk fringe; center front length (bodice): 57.9 cm (22 13/16 in), waist (bodice): 76 cm (29 15/16 in). Philadelphia: Philadelphia Museum of Art, 1938-18-12a, b. Gift of Mr. and Mrs. Ogden Wilkinson Headington in memory of Ogden D. Wilkinson, 1938. Source: PMA
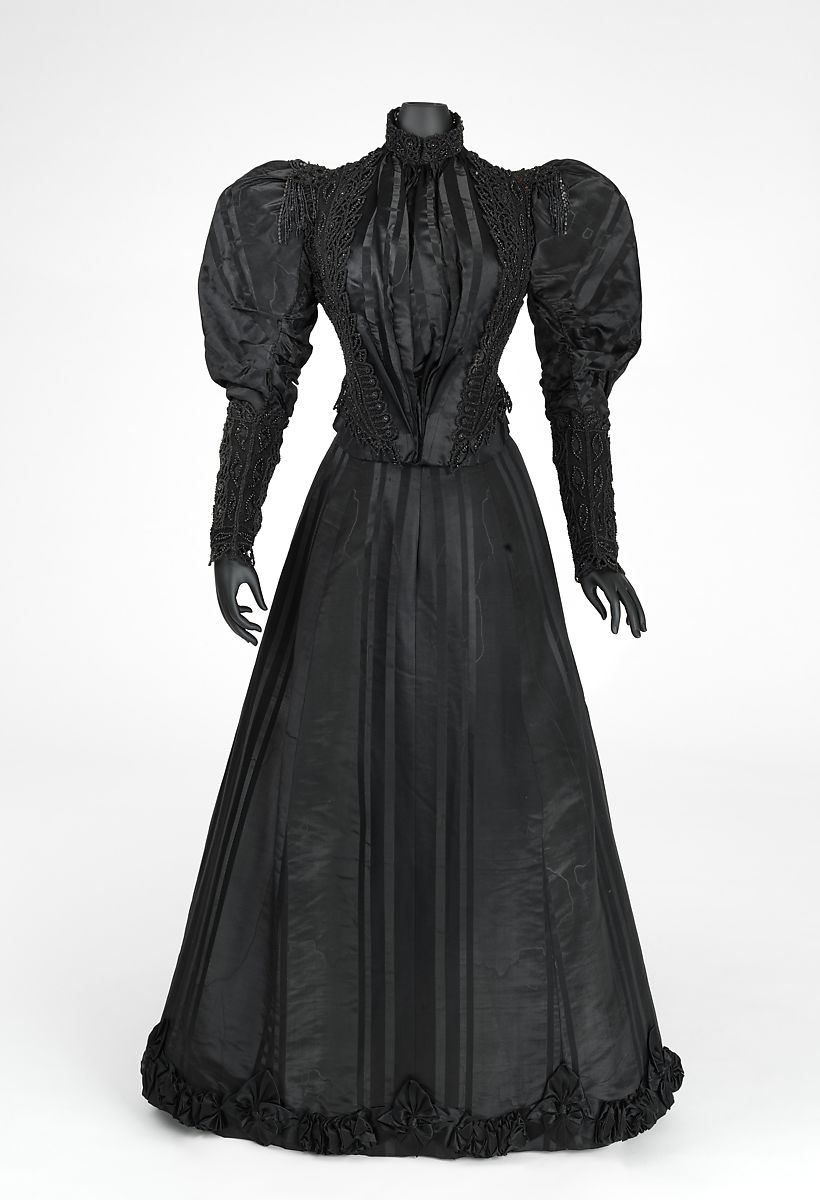
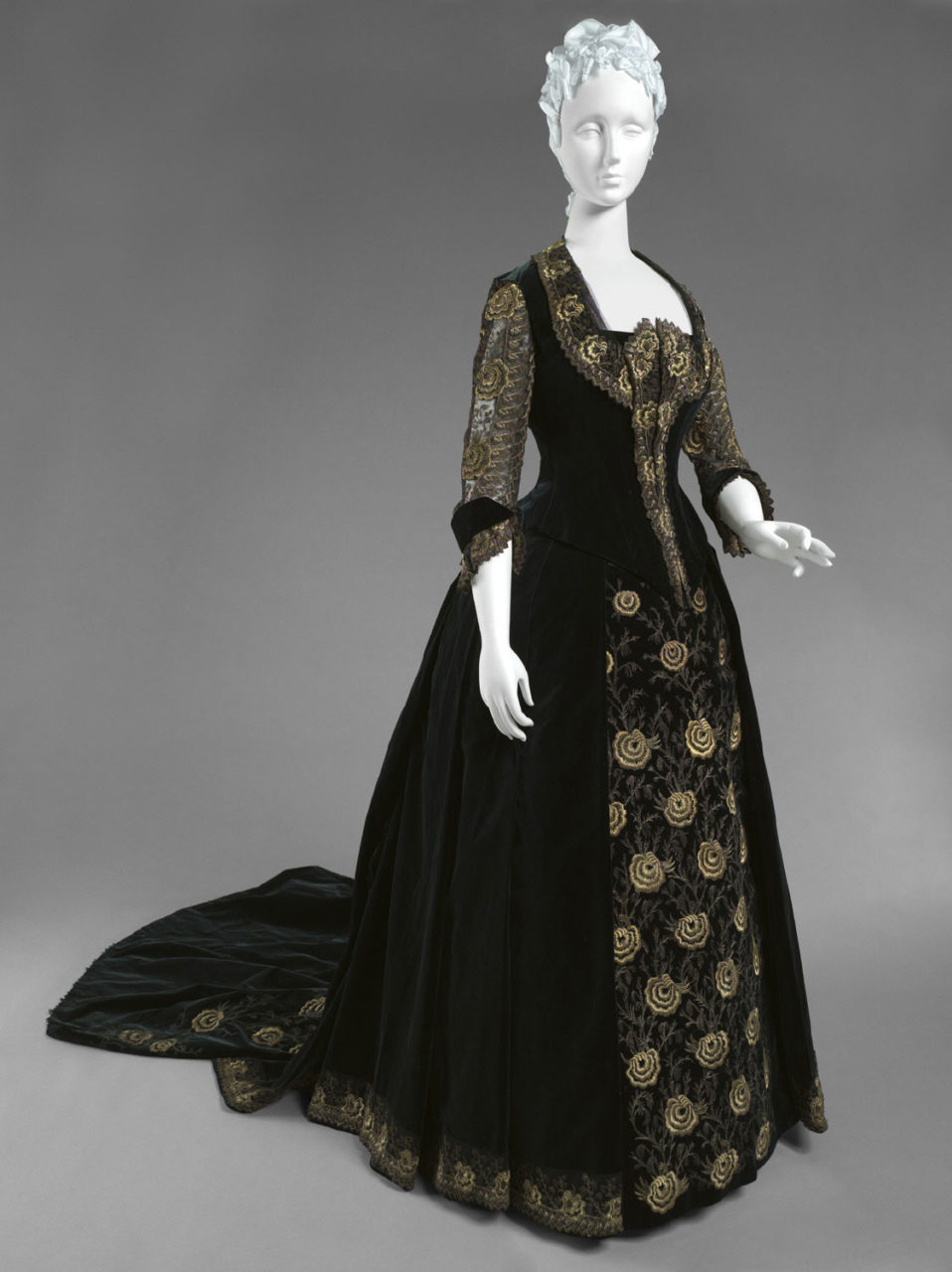
Emile Pingat (French, 1820-1901). Woman's dress with dinner and evening bodices, ca. 1885. Silk velvet, metallic thread embroidery, and machine-made lace; waist: 78.7 cm (31 in). Philadelphia: Philadelphia Museum of Art, 1949-29-3a--c. Gift of Mrs. Carroll S. Tyson, 1949. Source: PMA
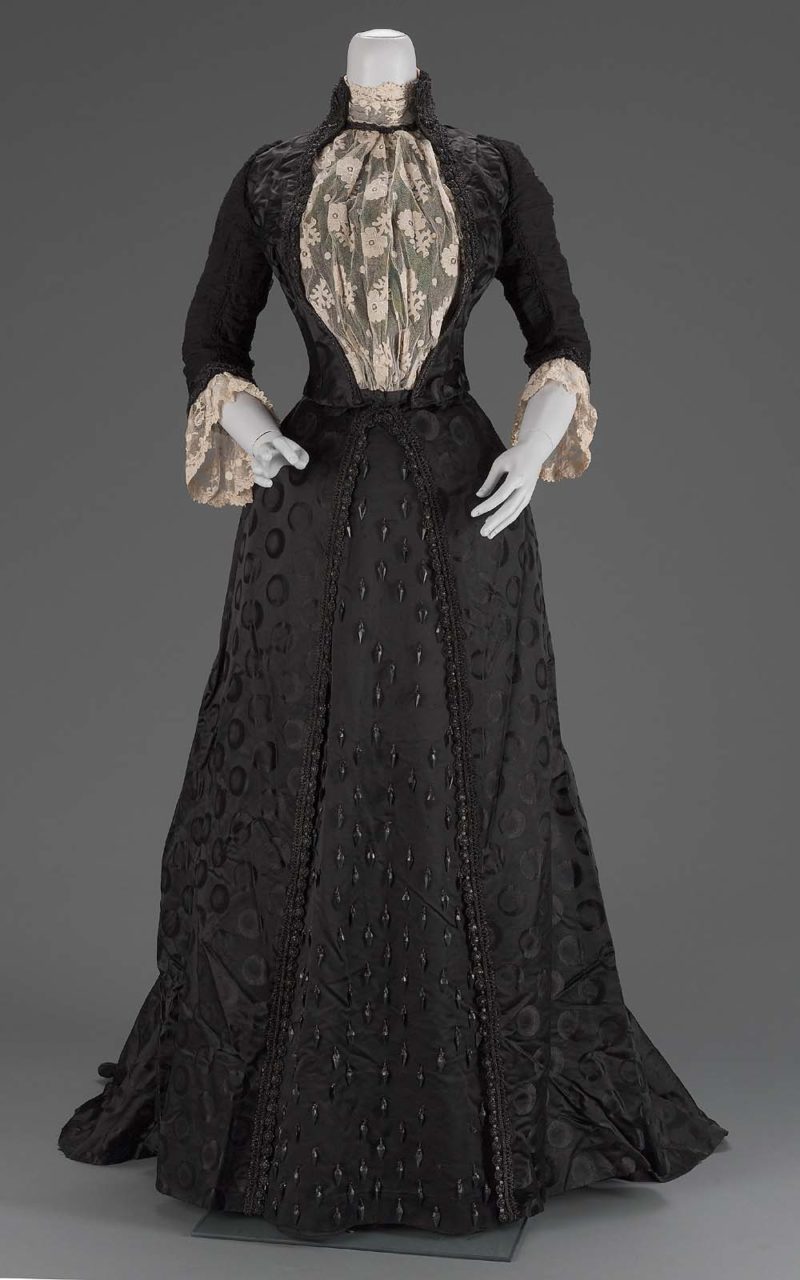
Emile Pingat (French, 1820-1901). Woman's dress, ca. 1889. Silk satin damask, silk plain weave (chiffon), silk appliquéd lace, glass beads; center back (bodice): 47 cm (18.5 in); length (skirt): 137.2 cm (54 in). Boston: Museum of Fine Arts, 2003.141.1-2. Gift of Ruth Oliver Jolliffe. Source: MFA Boston
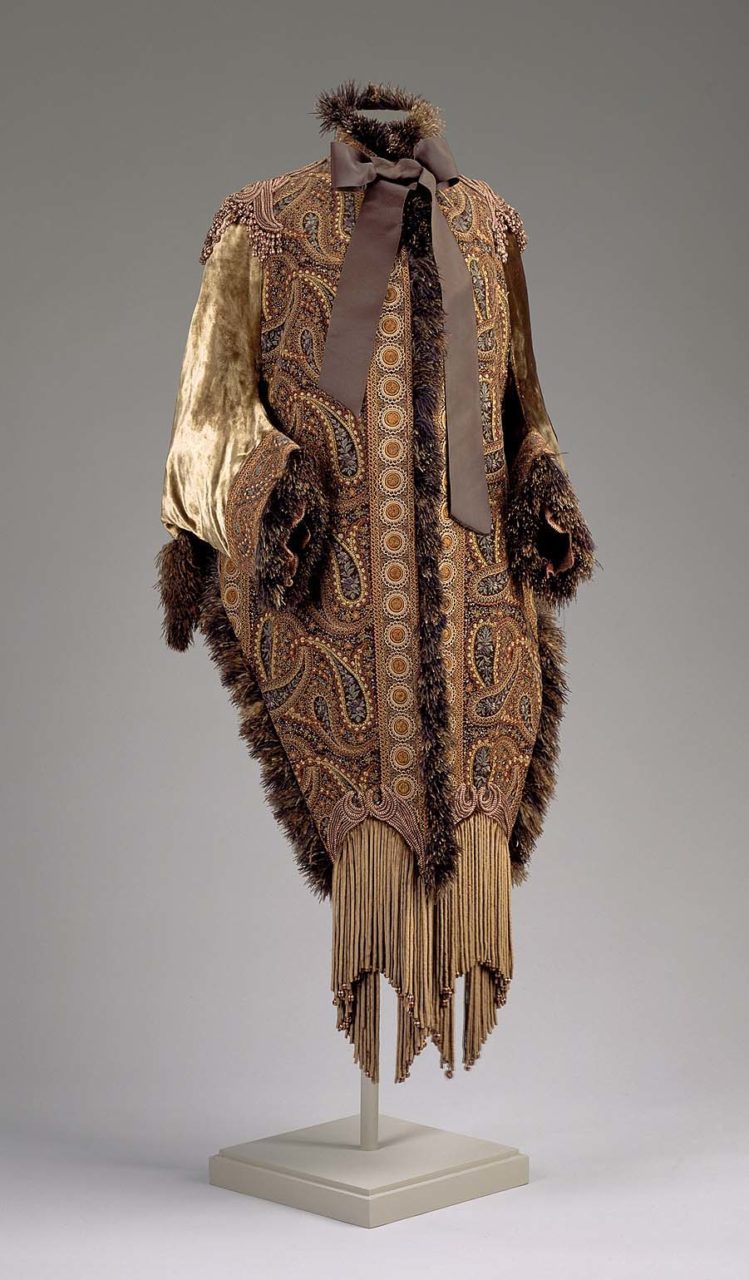
Emile Pingat (French, 1820-1901). Woman's dolman, ca. 1883-90. Silk; velvet embroidered with silk, silk lace, chenille fringe, feathers, silk braid; 60 cm (23 5/8 in). Boston: Museum of Fine Arts, 1972.911. Gift of Mrs. Norman J. Padelford. Source: MFA Boston
Emile Pingat (French, 1820-1901). Mantle, ca. 1891. Wool, silk, metal, feathers. New York: The Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2009.300.337. Gift of the Brooklyn Museum, 2009; Gift of Cornelia Gracie Henshaw, 1964. Source: The Met
To Learn More:
- “At Spring Openings.” Harper’s Bazar 25, no. 13 (March 26, 1892): 243, accessed 6 May 2016. http://hearth.library.cornell.edu/cgi/t/text/pageviewer-idx?c=hearth&cc=hearth&idno=4732809_1435_013&q1=pingat&frm=frameset&view=pdf&seq=3
- Coleman, Elizabeth Ann. The Opulent Era: Fashions of Worth, Doucet, and Pingat. London: Thames and Hudson, 1989.
- “French Breeding and Dressing.” Harper’s Bazar 8, no. 33 (August 16, 1884): 513-514, accessed 27 April 2016. http://hearth.library.cornell.edu/cgi/t/text/pageviewer-idx?c=hearth&cc=hearth&idno=4732809_1452_033&q1=pingat&frm=frameset&view=pdf&seq=2
- “Toilettes de Printemps de la Maison Pingat.” Revue Ilustrée 12, no. 44 (June 15, 1891): 27, accessed 19 May 2016. http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k6263995v/f39.image.r=maison%20pingat